
Fat over Lean... Thick Over Thin... Thick Over Lean... Whatever...
It’s Time to Get Rid of Them
Let’s toss out the concepts of “fat over lean” and, for that matter, “thick over thin” (or the confused “thick over lean”) while we are at it, and let’s consider the physical structure of the paint.
To understand the properties of oil paint, it is helpful to understand the relationship between the pigment and oil. One way to think about the relationship between pigment and binder is a brick wall. Every mason knows there is an ideal ratio of mortar to brick. Too much mortar and the wall is weak. Not enough mortar and the bricks fall apart.
The same relationship exists between the pigments and binder in dried paint. We call this relationship or ratio the pigment volume concentration or PVC. PVC is the volume of pigment compared to the volume of all solids. If the paint has a PVC of 30, then 30% of the total binder/pigment is pigment, and 70% is binder solids.
The point at which there is just enough binder to wet pigment particles is called the critical pigment volume concentration (cPVC). This is between 45% and 55% PVC for almost all colors. Films with lower pigment concentrations have more gloss, but as the PVC increases, they become increasingly matte. Films with high percentages of pigment are more permeable to moisture and susceptible to solvents. This is because, with more pigment, there is less binder to fill the voids between pigment particles. This porosity leaves the film open to the environment. Films with higher pigmentation have increasing lower tensile strength. (See the graph.)
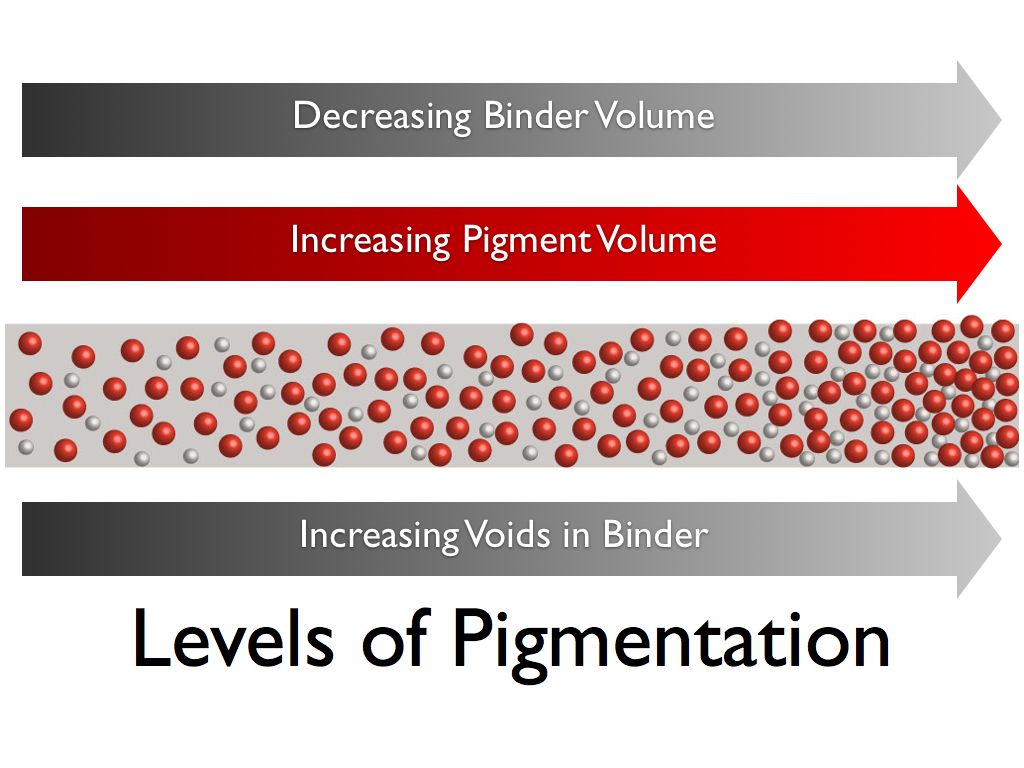

As the PVC increases past the cPVC, the dried paint film will contain voids. The porosity will increase, moisture vapor transmission will increase, and wet hiding will decrease, but dry hiding will increase. As the paint dries, a condition will exist where the paint has too much pigment and too little oil, such that the internal voids created will entrap air or solvent in the vapor phase.
Most paints in tubes contain enough binder to wet and envelope pigment particles, so they are at about the critical pigment volume concentration (cPVC) for that pigment or mixture of pigments. The variation in the pigment volume of particular colors between brands is due to the type of oil used, the amount of oil (some paint makers may choose to make their colors softer or thicker), and the amount of additives used in their formulation.
So, the best way to discuss paint is by understanding the relation between pigment and oil, expressed as the pigment volume concentration (PVC). Oil paint straight out of the tube is in the form of a paste and is usually near its cPVC. Adding oil to paste paint lowers the PVC (low PVC), while adding solvent potentially increases the PVC (high PVC). Hence, the ideal paint is a paint of the consistency of paste, and this is why the admonition to “apply thick paint thinly” or work with paste paint in thin layers is the best practice for oil painting.
From this, it is clear that paint consists of both liquid and solid components. In the case of oil paint, the liquid component is a drying vegetable oil. The oil undergoes chemical and physical processes that change it from a liquid to a solid, called “oxidative polymerization.” Oil is the binder or glue that holds the pigment particles together and onto a substrate.
You may think of paint as a pigmented or colored adhesive. When it comes to adhesion in oil paint, oil is the glue. While many artists believe that mechanical adhesion is most important when it comes to paint, what is more, important is “dispersive adhesion,” which does not rely on the absorption of the binder or oil into a porous substrate or on surface texture (although they can improve dispersive adhesion) but instead on surface energy and polarity. Hence, paste paint adheres better than paint that has been heavily diluted with a solvent (high PVC) even if it is partially absorbed into the substrate because the latter has less oil or glue to adhere pigment particles to the surface of the substrate.
Confusing Concepts in Oil Painting:
Fat Over Lean Explained
New Live Streaming Episode of Artist Materials Advisor
In this episode of Artist Materials Advisor, we examine how explanations of the fat-over-lean rule are more confusing than helpful. We explain the fat-over-lean rule and provide the actual physical properties behind the rule. With this new understanding, you will be freed from thinking about the rule in your painting practice.
The Artist Materials Advisor is a monthly online event where you can ask questions during the live stream event. This is a great opportunity to learn about art materials!
Fat Over Lean–A Better Interpretation
“Fat Over Lean” is a confusing concept at its best. It has been explained in so many ways. Artists use many different metaphors to explain the rule. Some even compare it to fat and lean ground beef. Yet few understand how to use it. In this Studio Tips course, we explain the fat-over-lean rule in a novel way that simplifies understanding and applying it in your oil painting.
This Studio Tips Live! event was broadcast on April 21, 2021, at 10:00 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time (5:00 UTC). You can watch the event now, along with an hour of questions and answers from participants. Enroll in this course now to access its content. After enrolling in this course, you have immediate access for the next thirty days.
Enroll in the Course
Frequently Asked Questions
Does fat over lean apply to acrylics?
The 'fat over lean' principle is specific to oil painting and does not apply directly to acrylics. Acrylic paint dries through water evaporation, unlike the oxidative process in oils. However, pigment volume concentration (PVC) applies to all paints.
What is the fat over lean ratio?
The fat over lean ratio refers to progressively increasing the oil content in the paint layers applied over each other to enhance flexibility and prevent cracking.
Is turpentine fat or lean?
Turpentine is considered 'lean' as it is a solvent that thins the oil paint, reducing its oil content and accelerating drying time.
Is damar varnish fat or lean?
Damar varnish is generally considered 'fat' due to its natural resin content, which increases the oiliness and gloss of the paint surface when mixed with oil paint. However, this interpretation is misleading because dammar varnish contains solvents, usually turpentine, that decrease the solid binder content. For this reason, we recommend not using the fat over lean rule in your painting technique but rather using pigment volume concentration.
Are alkyd mediums such as Liquin and Galkyd fat or lean?
Alkyd mediums are considered to be 'fat,' as they are resins that not only speed up drying while increasing the gloss of oil paints but contribute to the overall binder solids of the dried paint film. However, these mediums also contain solvents, so this interpretation may be misleading, as we discussed in our answer to the question about dammar varnish.











